Diagnostic Scan
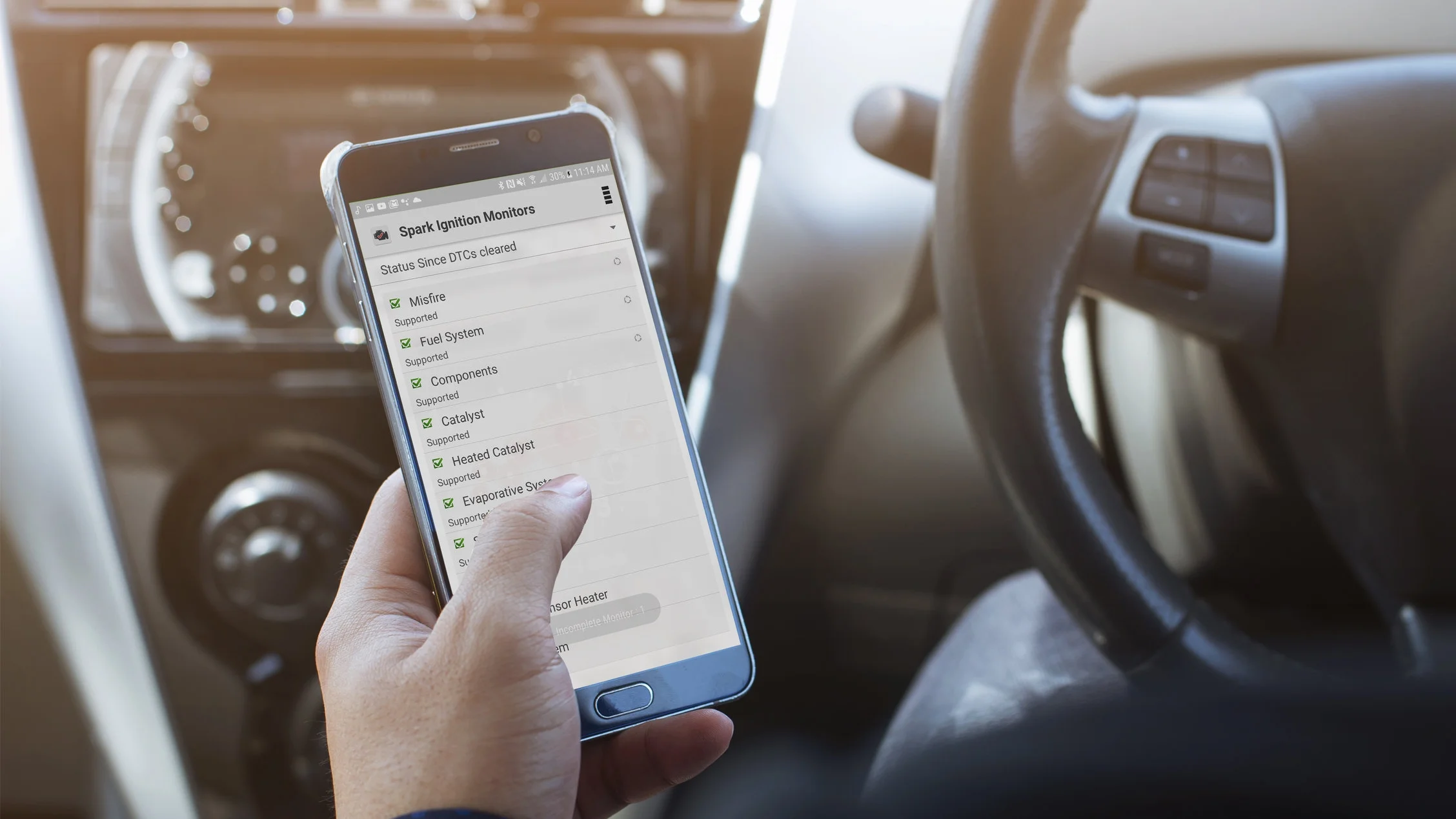
Diagnostic Scan Page is responsible for retrieving trouble codes from the vehicle's ECU and displaying to the screen. Additional dashboard parameters such as engine temperature, check engine light and gas tank volume are also displayed for supported vehicles.
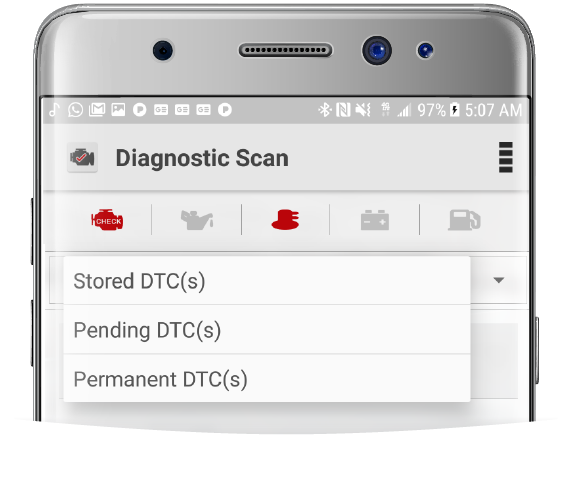
Diagnostic Scan Types
Stored Diagnostic Trouble Code
Pending Diagnostic Trouble Code: The pending DTC modules displays DTC that are currently in a pending state. Pending state means that the DTCs have only been detected during the current or last completed drive cycle and does not necessarily indicate a faulty component. The benefit of this module is that it displays DTC after a single drive cycle usually after a repair and clearing of the diagnostic information.
Permanent Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC)
The 3 categories of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are displayed when the DTC dropdown is clicked. The Stored DTC(s) is the default category.
NOTE : The volume of information displayed depends on what is supported by the vehicle manufacturer.
The Dashboard Parameters
The dashboard parameters are the check engine light, engine oil temperature, coolant temperature, battery voltage, and fuel tank volume displayed as icons under the title bar. The parameter limits can be configured in settings > Diagnostics Reports
Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Diagnostic Trouble Codes for a selected category are listed below the drop box. Information includes the Codes and its brief description.
A click on a specific trouble code displays the details and allow for more detailed internet searches. For more accurate results, the search string could be appended with the make, model and year of vehicle.
Adding mode, make and year to searches
Trouble Codes are generic. For a more specific search. The vehicles model make and year can be appended to the original search string.
Information such as possible causes of the trouble code and repair information can be found online. Videos are also provided on how the issue can be addressed.
How to Interprete Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Most of the diagnostic trouble codes do follow a standard format. The DTCs usually start with a letter, one of P, B C or U. The first letter indicates the System in the affected vehicle.
P - PowerTrain (engine transmission/gearbox)
P01 - Fuel and Air Metering
P02 - Injector Circuit
P03 - Ignition System or Misfire
P04 - Auxillary Emissions Control
P05 - Vehicle Speed Control and Idle Control System
P06 - Computer and Auxiliary Output Circuits
P07 - Transmission
P08 - Transmission
B - Body (includes A/C and air bag)
B00 - Body, including airbags and seatbelts
C - Chasis (includes ABS)
C00 - ABS
C01 - Brake Hydraulics
C02 - Wheel Speed Sensors and Traction Control
C03 - 4WD
C04 - Steering
C05 - Steering
C06 - Suspension and Leveling
C07 - Tire Pressure
C08 - Suspension and Leveling
U - User network (wiring bus/UART)
U00 - Communication Bus
U01 - Lost Communication With Sensor
U02 - Lost Communication With Sensor
U03 - Software Incompatibility
U04 - Invalid Data Received
The first digit after the letter indicates standard generic or manufacturer specific code. Standard codes have a first digit of 0 or 3, while manufacturer codes have first digits of 1 or 2.